ECCENTRIC TRAINING
STRETCH SHORTENING CYCLE Pt. 2
ECCENTRICS
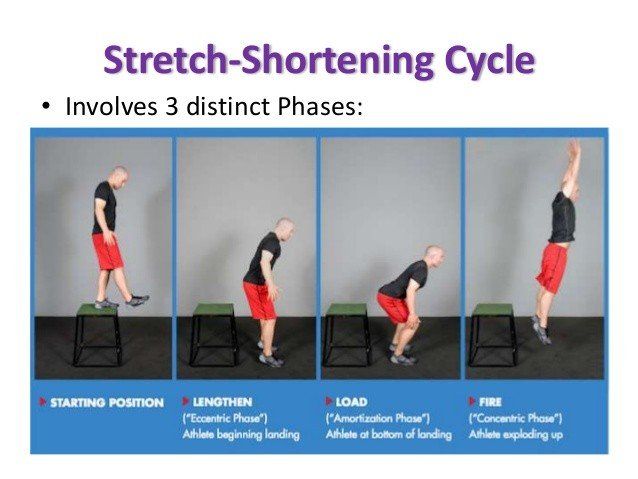
The eccentric phase is the lengthening/yielding portion of the stretch shortening cycle. It is the first phase of all dynamic movement and is when the muscle is stretched due to the force of an imposed load that is placed upon it. The isometric phase takes place immediately after the eccentric phase, then the concentric phase takes place last.
IMPORTANCE OF ECCENTRICS
It is during the eccentric phase of all movement that energy is stored to later be produced. An athlete’s force production capabilities are directly dependent upon their ability to absorb force. This is known as an athlete’s stretch reflex ability. Performing eccentric based movement will improve an athlete’s ability to absorb higher levels of force, which in turn will increase the amount of force they are able to produce.
If the athlete is unable to absorb high levels of force then there are two possible outcomes that can take place, both having negative affects on performance. First, there will be an energy “leak” during the eccentric phase of movement causing less energy to be produced during the concentric phase. Secondly, if an athlete puts themselves in a position where they will be experiencing high levels of force and they have not trained thoroughly, it is likely injury will occur overtime due to the lack of preparedness.
HOW TO IMPROVE THE STRETCH-REFLEX
An athlete’s ability to utilize their stretch-reflex is based on two different sensory receptors in the body, the muscle spindles and the golgi tendon organ (GTO).
The muscle spindles are responsible for sensing a change in the length of the muscle. As the muscle experiences a stretch, the muscle spindles activate the appropriate number of muscle fibers to create the required amount of force for the situation. The GTO senses the change in muscle tension. If the tension experienced by the muscle is determined to be too high by the GTO it will downregulate the muscle tension forcing it to relax. The GTO does this to prevent injury from occurring. Overall, the muscle spindles activate the necessary muscle fibers for the force experienced and the GTO deactivates muscle fibers if it senses to much force is being produced.
The GTO is known as being overprotective and for not letting the muscle spindles produce the forces they are is truly capable of. The implementation of eccentric training inhibits the effects of the GTO by downregulating its ability to decrease muscle tension. It also increases the muscle spindle response allowing more muscles to be activated. Both of these aspect lead to improved neuromuscular synchronization of the stretch-reflex and CNS, allowing for more force to be produced.
ECCENTRIC TRAINING BENEFITS
·Recruits more Type 2 (Fast Twitch) muscle fibers
·Eccentrically can handle up to 50% heavier loads than concentrically
·Improves force absorption capabilities
·Improves force production capabilities
·Downregulates GTO
·Upregulates muscle spindles
·Allows for increased time under tension
·Decreased risk of injury
Source
- Triphasic Lacrosse
By: Cal Dietz & Matt Van Dyke